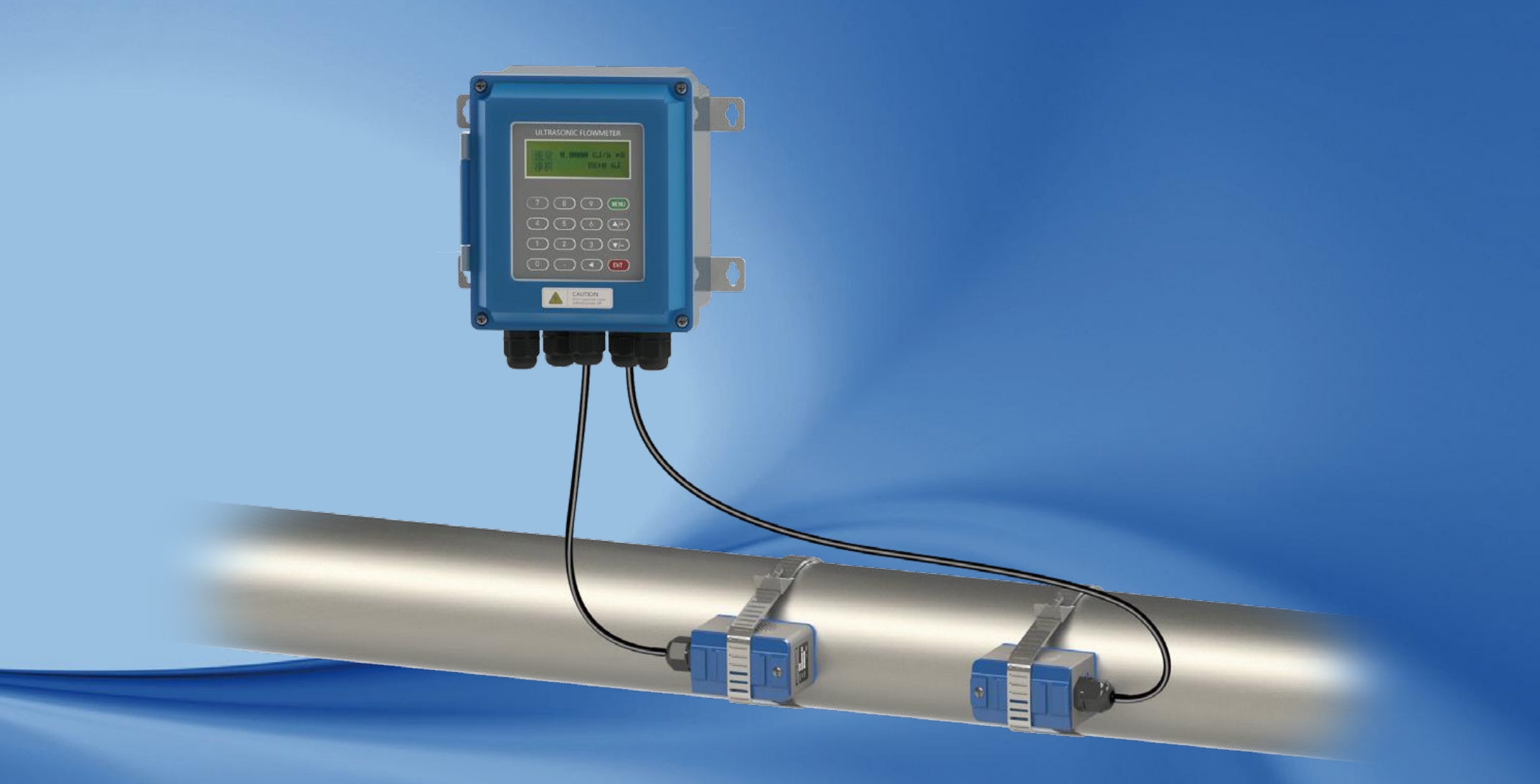
Application Scheme for External Clamp-on Ultrasonic Flowmeters
Background:
In various industrial sectors and municipal projects, flow measurement is a critical task. The external clamp-on ultrasonic flowmeter, as an advanced flow measurement device, stands out due to its non-contact measurement and easy installation features, offering unique market advantages. This scheme is developed to promote the effective application of such flowmeters.
Analysis of Key Features:
Non-Contact Measurement
Sensors are installed on the outer wall of the pipeline without damaging the structure or direct contact with the fluid.
Ideal for corrosive, flammable, or explosive media, avoiding corrosion and wear issues common with traditional contact-based flowmeters.
Extends equipment lifespan and ensures safety in hazardous environments.
Easy Installation
No need for pipe cutting, welding, or complex operations; sensors are fixed to the pipe surface per guidelines.
Reduces installation time and costs, minimizes disruption to production, and allows installation/maintenance without shutdown.
Broad Measurement Range
Supports pipe diameters from centimeters to meters and wide flow velocity ranges.
Versatile for diverse industrial applications, including high/low flow scenarios.
High Precision
Utilizes advanced ultrasonic technology for accurate flow measurement.
Achieves high precision under optimal conditions, providing reliable data for process control and metering.
Portability
Some models are portable, enabling temporary measurements or (patrol inspections) in variable locations.
Suitable for debugging, troubleshooting, and irregular measurement tasks.
Application Scenarios & Design
Industrial Process Monitoring
Use Cases: Chemical, power, and metallurgy industries.
Example: Measuring corrosive fluids (e.g., acids, alkalis) in large-diameter pipelines.
Implementation: Select sensors based on pipe material, diameter, and medium properties; integrate with control systems for real-time monitoring.
Heat Metering in Heating Systems
Use Cases: District heating networks.
Example: Measuring hot water flow for billing and system optimization.
Implementation: Combine with temperature sensors for heat calculation; transmit data to management systems for efficient parameter adjustment.
Water Resource Management
Use Cases: Urban water supply and wastewater treatment.
Example: Detecting leaks in water networks or monitoring flow in treatment plants.
Implementation: Install flowmeters at critical nodes to ensure data-driven process control.
Implementation Steps
Pre-Installation Survey
Gather user requirements (medium, pipe parameters, precision, environment).
Conduct on-site inspections to assess installation feasibility.
Device Selection
Choose flowmeter models based on survey results to meet technical and operational needs.
Installation & Calibration
Follow manufacturer guidelines for sensor placement and wiring.
Calibrate post-installation to ensure data accuracy.
System Integration
Integrate flowmeters with control or data acquisition systems for real-time data transmission.
Training & Maintenance
Train users on operation and maintenance.
Establish a maintenance schedule and responsive after-sales support.
Benefit Assessment.Economic Benefits
Lowers installation costs and downtime.
Enhances production efficiency and reduces energy waste.
Enables accurate billing in heating/water systems, improving revenue.
Social Benefits
Optimizes resource utilization and reduces environmental pollution.
Improves heating quality and public living conditions.
Prevents water waste through leak detection, supporting sustainable urban development.
Conclusion:
The external clamp-on ultrasonic flowmeter offers significant advantages in industrial, heating, and water management sectors. This scheme outlines tailored solutions for diverse applications, implementation steps, and benefit evaluations. By adopting this approach, users can achieve efficient, precise flow measurement while balancing economic and social benefits.